Shanghai's Rising Star: The Transformation of Pudong into a Global Financial Hub
⏱ 2025-05-06 07:28 🔖 上海龙凤419
📢0℃
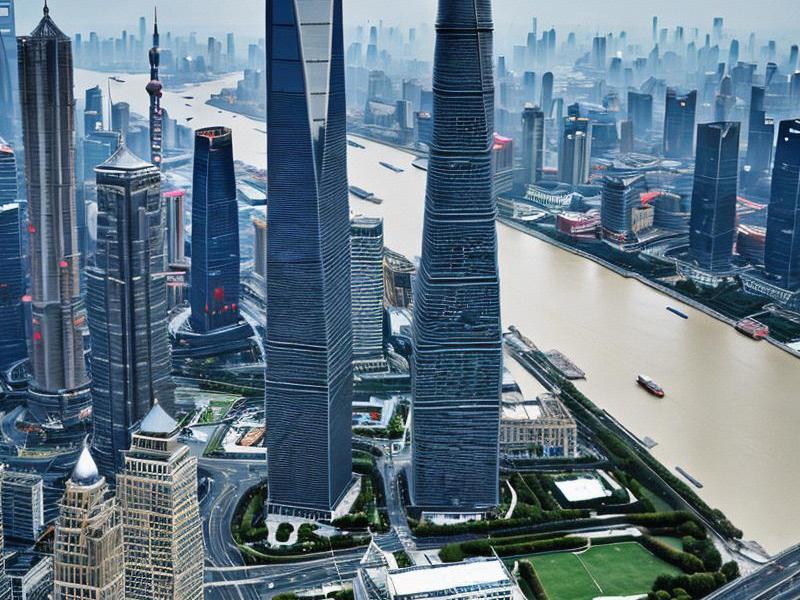

In the late 20th century, Pudong was a vast expanse of farmland and marshland on the eastern bank of the Huangpu River in Shanghai. Today, it stands as a symbol of China's economic miracle, a bustling financial district that rivals the world's most prestigious financial centers. The transformation of Pudong is not just a testament to Shanghai's urban development but also a microcosm of China's broader economic reform and opening up.
The story of Pudong's rise began in 1990 when the Chinese government made a bold decision to designate this area as a Special Economic Zone (SEZ). This strategic move aimed to attract foreign investment, promote technological innovation, and drive economic growth. The establishment of the Pudong New Area marked a new chapter in Shanghai's history and set the stage for its transformation into a global financial hub.
One of the key factors behind Pudong's success is its strategic location. Situated opposite the historic Bund, which has long been a symbol of Shanghai's international trade and finance, Pudong benefits from its proximity to the city's established business and cultural heart. This location advantage has facilitated the seamless integration of Pudong with the rest of Shanghai, creating a dynamic and interconnected urban environment.
The development of Pudong was driven by massive infrastructure investments. The construction of the Pudong International Airport, which opened in 1999, provided a world-class transportation hub that connected Shanghai to major cities around the globe. The completion of the Nanpu Bridge and the Yangpu Bridge in the late 1990s further enhanced Pudong's accessibility, linking it to other parts of Shanghai and the surrounding region.
The iconic skyline of Pudong, dominated by the Oriental Pearl Tower, the Jin Mao Tower, and the Shanghai World Financial Center, is a visual representation of the area's rapid development. These skyscrapers house some of the world's leading financial institutions, multinational corporations, and international organizations. The Lujiazui Financial District, located at the heart of Pudong, has become a global center for banking, insurance, and securities trading.
爱上海419论坛
Pudong's transformation has been supported by a series of policy measures aimed at creating a favorable business environment. The Chinese government has implemented tax incentives, simplified administrative procedures, and provided land and infrastructure support to attract foreign investors. These policies have helped Pudong establish itself as a hub for international finance, trade, and technology.
The influx of foreign investment has played a crucial role in Pudong's development. Multinational corporations such as HSBC, Citibank, and JPMorgan Chase have established their regional headquarters in Pudong, taking advantage of the area's business-friendly environment and strategic location. These companies have brought with them advanced technologies, management expertise, and global networks, contributing to the growth and competitiveness of Pudong's financial sector.
In addition to attracting foreign investment, Pudong has also focused on fostering domestic innovation and entrepreneurship. The establishment of the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park in 1992 has provided a fertile ground for high-tech enterprises and research institutions. This park has become a hub for biotechnology, information technology, and new materials, driving innovation and economic growth in Pudong.
The transformation of Pudong has had a profound impact on Shanghai and the broader Yangtze River Delta region. As a global financial hub, Pudong has enhanced Shanghai's status as an international metropolis and a key player in the global economy. The area's development has also contributed to the economic integration of the Yangtze River Delta region, fostering regional cooperation and competitiveness.
上海龙凤419社区
The success of Pudong has inspired other cities in China to pursue similar development strategies. Many cities have established SEZs and economic development zones, aiming to replicate Pudong's success and drive local economic growth. The experience of Pudong serves as a valuable lesson in urban planning, infrastructure development, and policy implementation.
However, the rapid development of Pudong has also brought challenges and issues that need to be addressed. The rapid urbanization process has led to concerns about environmental sustainability, social inequality, and the preservation of cultural heritage. The high density of skyscrapers and the influx of people have created pressure on transportation, housing, and public services.
To address these challenges, the Shanghai municipal government has implemented a series of measures aimed at promoting sustainable development and improving the quality of life in Pudong. These measures include the development of green spaces, the promotion of public transportation, and the enhancement of social welfare programs. The government has also emphasized the importance of preserving Pudong's historical and cultural heritage, ensuring that the area's development is balanced and inclusive.
The transformation of Pudong is not just a story of economic growth and urban development but also a story of China's commitment to reform and opening up. Pudong's success demonstrates the potential of China's economic model and its ability to adapt to the challenges of globalization. The area's transformation has inspired confidence in China's future and its role in the global economy.
上海龙凤419
As Pudong continues to evolve, it faces new opportunities and challenges in the context of a rapidly changing global landscape. The rise of digital technologies, the growth of the green economy, and the increasing importance of sustainable development are shaping the future of Pudong and the global financial industry. The area's ability to adapt to these changes will determine its continued success and relevance in the years to come.
In conclusion, the transformation of Pudong from a rural area to a global financial hub is a remarkable achievement that reflects Shanghai's urban development and China's economic reform and opening up. The strategic location, massive infrastructure investments, favorable business environment, and influx of foreign investment have contributed to Pudong's success. However, the area also faces challenges related to environmental sustainability, social inequality, and cultural heritage preservation.
The experience of Pudong serves as a valuable lesson for other cities in China and around the world, demonstrating the potential of urban development and economic reform. As Pudong continues to evolve, it will play a crucial role in shaping the future of Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta region, and China's global economic standing. The story of Pudong is a testament to the resilience and determination of the Chinese people in their pursuit of prosperity and progress.
【潮涌长三角:上海的半径与圆周】从外滩灯光到江南水乡的共生密码Shanghai's Vibrant Cultural Scene: A Blend of Tradition and Modernity【霓虹与素笺】上海女性的百年气质图谱Shanghai 5250: Quantum Leisure Singularity and the Galactic Nightlife Matrix【城市观察】文化魔方的三原色:上海剧场、书店与美术馆的共生实验Shanghai's Nightlife Renaissance: Where Imperial Heritage Meets Quantum Innovation【霓虹密码】上海娱乐会所的时空折叠术Shanghai's Smart Nightlife Ecosystems: Blending Imperial Heritage with AI-Driven Innovation【量子上海】在11个维度中同时绽放的魔都镜像(1850-2025)Shanghai's Finest Women: A Story of Resilience and Excellence